Publication of a recent study published in Cell Stem Cell by Team 10 on the protective effect of PAX3 in response to dioxin exposure!
 A recent study conducted by Audrey Der Vartanian (post-doctoral researcher) and Marianne Gervais-Taurel (CNRS researcher) in the team of Pr. Frédéric Relaix (Team 10, IMRB) reveals that the transcription factor PAX3 protects a subpopulation of adult skeletal muscle stem cells in response to chronic exposure to an environmental pollutant, dioxin, with harmful effects on health. This study was published in CELL STEM CELL on April 18, 2019.
A recent study conducted by Audrey Der Vartanian (post-doctoral researcher) and Marianne Gervais-Taurel (CNRS researcher) in the team of Pr. Frédéric Relaix (Team 10, IMRB) reveals that the transcription factor PAX3 protects a subpopulation of adult skeletal muscle stem cells in response to chronic exposure to an environmental pollutant, dioxin, with harmful effects on health. This study was published in CELL STEM CELL on April 18, 2019.
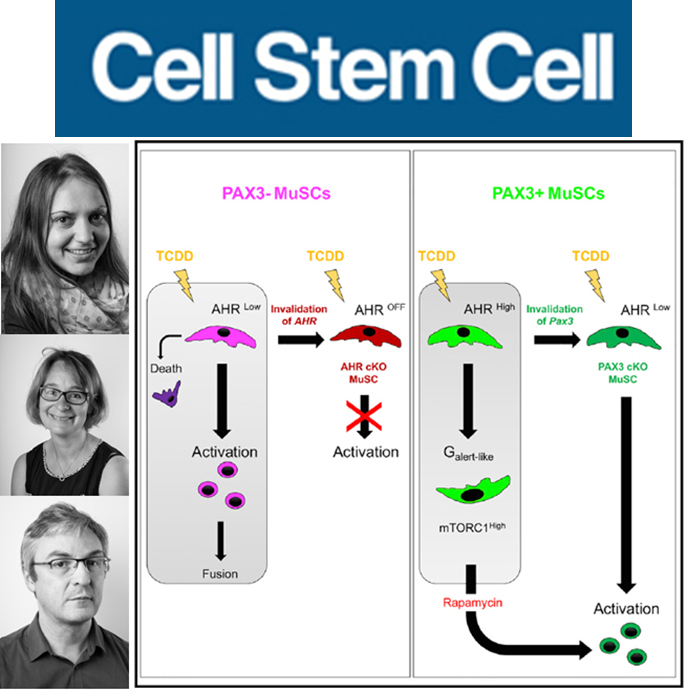
Skeletal muscle has an important capacity for regeneration following traumatic damage or in neuromuscular pathologies. While it has been demonstrated that this property is conferred by muscle stem cells, satellite cells, all the mechanisms regulating their function are still far from being understood. A subpopulation of these stem cells express the transcription factor PAX3. Although the function of PAX3 during development has already been studied, its role in adult muscle is unknown.
This study reveals a differential response of satellite cells expressing PAX3 in response to systemic exposure to dioxin. Dioxin is one of the most toxic and persistent environmental pollutants whose harmful consequences for the body are induced by the Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AHR) signalling pathway. In mice, Professor Frédéric Relaix’s team has demonstrated that chronic exposure to dioxin causes the progressive loss of satellite cells that do not express PAX3.
On the other hand, satellite cells expressing PAX3 are able to resist environmental stress, leaving their quiescence state but protected from the harmful consequences of dioxin by activating the mTORC1 pathway giving them a special status, called the G (alert) state downstream of PAX3.
This work reveals an unexpected impact of pollution on stem cell function and opens new perspectives on an innovative molecular mechanism to resist environmental stress.
Link to the article: https://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/fulltext/S1934-5909(19)30118-3

