Genomic Group
 Research topics:
Research topics:
It is widely demonstrated that genetic factors strongly contribute to the risk of developing most psychiatric disorders. Our group has been working for many years on the characterization of the genetic architecture of bipolar disorders, schizophrenia or major depressive disorders as well as on the identification of genetic and biological markers that would allow to predict the evolution of the disease or to select the most adapted treatment to the physiology of the ill persons. Our exploration is based mainly on high-throughput genotyping, exome or genome sequencing, transcriptome and methylome analyses.
In recent years, we have developed three lines of research around (i) the genetic architecture of psychiatric disorders in order to estimate the individual risk of developing a disorder or responding to a treatment, (ii) the links between genetic factors and molecular mechanisms that are at the origin of these disorders, in particular through the development of animal models and brain organoids, and (ii) the exploration of environmental factors in the vulnerability to psychiatric disorders, with research on the effects of air pollution on brain development and the risk of developing a psychiatric disorder.
 Recent results:
Recent results:
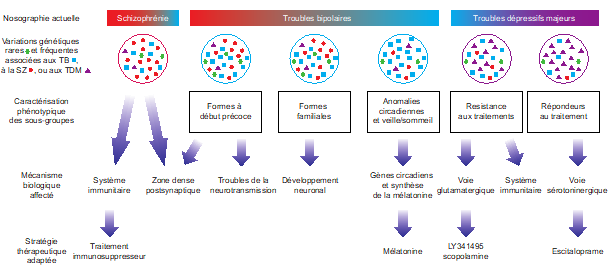
Our contribution with many other research groups to the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium has allowed in recent years the identification of numerous loci associated with the risk of developing bipolar disorder (Jamain et al., 2014; Mullins et al., 2021), but also to show the genetic links that exist between bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and major depressive disorder (Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium, 2019; Courtois et al., 2020). We have thus been able to characterize clinically homogeneous subgroups that exhibit dysfunction of the same molecular mechanisms.
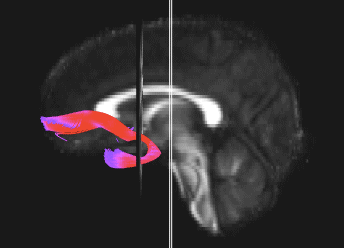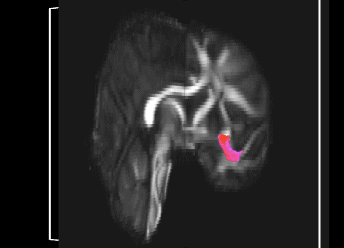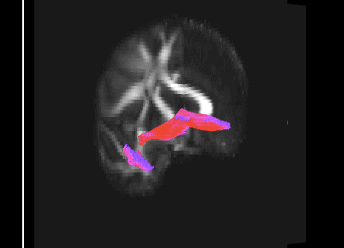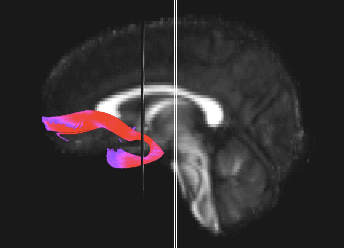
Bundle showing functional connectivity between the ventromedial prefrontal cortex and the amygdala. The risk genotype of rs6039769 located in the promoter of SNAP25 is associated with an increase in this connectivity in men.
Functional exploration of rare and frequent genetic variations associated with bipolar disorder revealed to us the importance of neurotransmitter mechanisms in individuals with early-onset forms of bipolar disorder (Etain et al., 2010; Houenou et al., 2017). In particular, we showed that these mechanisms were associated with changes in the structure of the amygdala and the connectivity between it and the ventromedial prefrontal cortex in individuals carrying genotypes at risk for developing bipolar disorder in the SNAP25 gene (Houenou et al. 2017). We also showed that genetic variations altering the function of CADPS, a calcium-sensitive protein required for neurotransmitter release, were associated with increased sensitivity to stress in both humans and mice (Sitbon et al. in press).
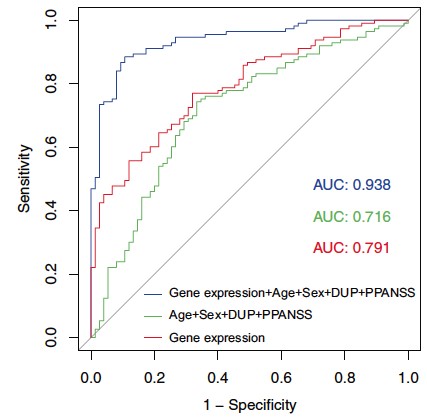 Through the genetic characterization of homogeneous subgroups of people with psychiatric disorders sharing vulnerability factors, our objective is to propose therapeutic strategies adapted to the molecular mechanisms disrupted in sick people. In this sense, we have shown that the expression of certain genes in the peripheral blood can predict the response to antipsychotic treatment during a first episode of psychosis and that this prediction is even more reliable when combined with clinical and environmental data collected in patients (Troudet et al., 2020).
Through the genetic characterization of homogeneous subgroups of people with psychiatric disorders sharing vulnerability factors, our objective is to propose therapeutic strategies adapted to the molecular mechanisms disrupted in sick people. In this sense, we have shown that the expression of certain genes in the peripheral blood can predict the response to antipsychotic treatment during a first episode of psychosis and that this prediction is even more reliable when combined with clinical and environmental data collected in patients (Troudet et al., 2020).
Selected publications
Mullins N, Forstner AJ, O'Connell KS, Coombes B, Coleman JRI, et al. Genome-wide association study of more than 40,000 bipolar disorder cases provides new insights into the underlying biology.
Nat Genet. 2021 Jun;53(6):817-829. doi: 10.1038/s41588-021-00857-4.Schürhoff F, Corfdir C, Pignon B, Lajnef M, Richard JR, Marcos E, Pelissolo A, Leboyer M, Adnot S, Jamain S, Szöke A. No alteration of leukocyte telomere length in first episode psychosis.
Psychiatry Res. 2021 Jul;301:113941. doi: 10.1016/j.psychres.2021.113941.Pollak TA, Vincent A, Iyegbe C, Coutinho E, Jacobson L, Rujescu D, Stone J, Jezequel J, Rogemond V, Jamain S, Groc L, David A, Egerton A, Kahn RS, Honnorat J, Dazzan P, Leboyer M, McGuire P. Relationship Between Serum NMDA Receptor Antibodies and Response to Antipsychotic Treatment in First-Episode Psychosis.
Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Jul 1;90(1):9-15. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.11.014.El Yacoubi M, Vaugeois JM, Jamain S. Antidepressant-like effect of low dose of scopolamine in the H/Rouen genetic mouse model of depression.
Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2021 Aug;35(4):645-649. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12639.Szoke A, Pignon B, Boster S, Jamain S, Schürhoff F. Schizophrenia: Developmental Variability Interacts with Risk Factors to Cause the Disorder: Nonspecific Variability-Enhancing Factors Combine with Specific Risk Factors to Cause Schizophrenia.
Bioessays. 2020 Nov;42(11):e2000038. doi: 10.1002/bies.202000038.Troudet R, Ali WBH, Bacq-Daian D, Rossum IWV, Boland-Auge A, Battail C, Barau C; OPTiMiSE study group, Rujescu D, McGuire P, Kahn RS, Deleuze JF, Leboyer M, Jamain S. Gene expression and response prediction to amisulpride in the OPTiMiSE first episode psychoses.
Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Sep;45(10):1637-1644. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0703-2.Courtois E, Schmid M, Wajsbrot O, Barau C, Le Corvoisier P, Aouizerate B, Bellivier F, Belzeaux R, Dubertret C, Kahn JP, Leboyer M, Olie E, Passerieux C, Polosan M, Etain B, Jamain S; and the FondaMental Advanced Centers of Expertise in Bipolar Disorders (FACE-BD). Contribution of common and rare damaging variants in familial forms of bipolar disorder and phenotypic outcome.
Transl Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 28;10(1):124. doi: 10.1038/s41398-020-0783-0.Cross-Disorder Group of the Psychiatric Genomics Consortium. Genomic Relationships, Novel Loci, and Pleiotropic Mechanisms across Eight Psychiatric Disorders.
Cell. 2019 Dec 12;179(7):1469-1482.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.11.020.Houenou J, Boisgontier J, Henrion A, d'Albis MA, Dumaine A, Linke J, Wessa M, Daban C, Hamdani N, Delavest M, Llorca PM, Lançon C, Schürhoff F, Szöke A, Le Corvoisier P, Barau C, Poupon C, Etain B, Leboyer M, Jamain S. A Multilevel Functional Study of a SNAP25 At-Risk Variant for Bipolar Disorder and Schizophrenia.
J Neurosci. 2017 Oct 25;37(43):10389-10397. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1040-17.2017.Jamain S, Cichon S, Etain B, Mühleisen TW, Georgi A, Zidane N, Chevallier L, Deshommes J, Nicolas A, Henrion A, Degenhardt F, Mattheisen M, Priebe L, Mathieu F, Kahn JP, Henry C, Boland A, Zelenika D, Gut I, Heath S, Lathrop M, Maier W, Albus M, Rietschel M, Schulze TG, McMahon FJ, Kelsoe JR, Hamshere M, Craddock N, Nöthen MM, Bellivier F, Leboyer M. Common and rare variant analysis in early- onset bipolar disorder vulnerability.
PLoS One. 2014 Aug 11;9(8):e104326. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104326.