
 Latest news from the team
Latest news from the team
 March 20, 2024
March 20, 2024
The PolluRisk platform honored by the Ile-de-France Region as part of the 30th anniversary of the SESAME system. The main objective of the SESAME system is to make the Ile-de-France region a world reference in science and technology by giving laboratories the necessary means to develop new projects and to implement original experimental research systems. More informations
 March 14, 2024
March 14, 2024
Congratulations to Khadeeja Adam SY, GEIC2O team, winner of the prize for best active participation at the 17th European CF Young investigators’ Meeting! Learn more
 February 12, 2024
February 12, 2024
Congratulations to Benjamin Simonneau from Pascal Fanen’s group, in the GEIC20 team, who was awarded the prize for best poster at the Colloque Jeunes Chercheurs organised by the patient association Vaincre la Mucoviscidose on Tuesday 6 February 2024! To find out more
 January 25, 2024
January 25, 2024
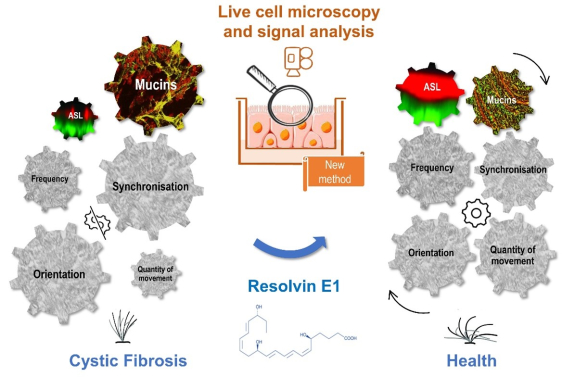
Corrective role of resolvin E1 in ciliary dyskinesia in cystic fibrosis, a study published in PNAS by Valérie URBACH’s group, Sophie LANONE’s team. More info
 May 9, 2023
May 9, 2023
Congratulations to Sophie Lanone of IMRB’s GEIC2O team and Patrice Coll of LISA-UPEC/UPCité/CNRS, for their article “Air pollution, so complex to reproduce in the laboratory” in the Figaro Santé on Monday May 8! Read more on Le Figaro Santé, Monday, May 8, 2023
 Research theme:
Research theme:
The general scientific objective of GEIC2O team is to understand the interplay between genetic and environmental factors in the development of lung diseases throughout the life (namely from children to adults).
We particularly focus on lung diseases of non-genetic (Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease or COPD) and genetic (Cystic Fibrosis and surfactant disorders) origins.
The large pluridisciplinarity of GEIC2O team staff comprising MD (lung specialists – adult and pediatricians, occupational medicine, geneticists, ear/nose/throat specialists, and lung pathologist) as well as PhD (in cellular and molecular biology, biochemistry, genetic, bioinformatics and respiratory physiology) allows us to develop a comprehensive scientific approach ranging from in vitro experimental work to preclinical models and patient cohorts.
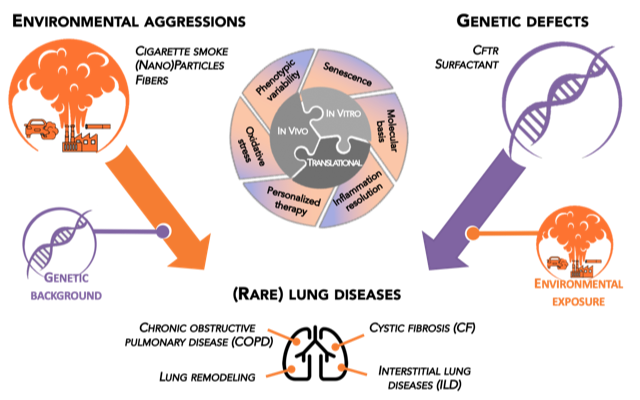
 Four main research axes:
Four main research axes:
- Molecular bases of cigarette smoke-induced COPD
- Genetic and cellular bases of CF and surfactant disorders
- Resolution of inflammation in lung diseases
- Environmental aggressions and course of lung diseases
 Fundings:
Fundings:
 EU (COST actions, H2020 REMEDIA – http://www.h2020-remedia.eu/), ANR, Programme d’investissement d’avenir (LabEx SERENADE https://serenade.cerege.fr, EquipEx NanoID – http://nano-id.fr/), ANSES, Chancellerie des Universités, Vaincre la Mucoviscidose, Centre de compétence en Nanosciences d’île de France (C’Nano), Société de pneumologie de langue française (SPLF), Île de France Region (DIM QI2 – https://www.dim-qi2.fr/, SESAME, …), …
EU (COST actions, H2020 REMEDIA – http://www.h2020-remedia.eu/), ANR, Programme d’investissement d’avenir (LabEx SERENADE https://serenade.cerege.fr, EquipEx NanoID – http://nano-id.fr/), ANSES, Chancellerie des Universités, Vaincre la Mucoviscidose, Centre de compétence en Nanosciences d’île de France (C’Nano), Société de pneumologie de langue française (SPLF), Île de France Region (DIM QI2 – https://www.dim-qi2.fr/, SESAME, …), …
 Main results:
Main results:
- Resolvin E1 and lipoxin B4, two lipid mediators of the resolution of inflammation, correct the secondary ciliary dyskinesia observed in the airway epithelium of Cystic Fibrosis patients (Briottet et al, 2024).
- Respiratory epithelial cells from patients with Cystic Fibrosis have a reduced capacity to produce several lipid mediators of inflammation resolution (lipoxins, resolvins, protectins and maresins). This phenomenon is worsened for CF women (Shum et al, 2022) (Urbach et al, 2023).
- Role of new molecular mechanism (PGE2, p53, mesenchymal stem cell features of lung fibroblasts) in COPD pathophysiology (Thorax 2018, Cell Death Dis 2018, JACI 2017, AJRCMB 2016, Arch Toxicol 2015, AJRCCM 2013)
- Implementation of a new strategy, which combines in silico and in vitro analyses to anticipate the occurrence of “splicing-causing” mutations in CFTR exons (Human Mutat 2014, 2013)
- First description of the molecular mechanism of an exonic SFTPC mutation, which unmasked a splicing defect (Eur J Human Genet 2017)
- Expansion of the phenotypic spectrum of interstitial lung disease i.e. due to NKX2-1 or ABCA3 mutations (Respir Med 2017, ERJ 2014)
- Step towards personalized therapy of CF, with the identification of new therapeutic targets (Br J Pharmacol 2016, Hum Mutat 2013, Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2013)
- Identification of the relations between asbestos exposure, pleural plaques, and occurrence of mesothelioma, lung cancer or colon cancer in asbestos-exposed patients (EHP 2017, ERJ 2014, AJRCCM 2014, J Natl Cancer Inst 2014)
- First evidence of respiratory consequences of occupational exposure to metal NP in welders ( Rep. 2018, Nanotoxicology 2016, Particle & Fibre Toxicol 2014)
- Long-term effects of maternal exposure to environmental contaminants (cigarette smoke, metal nanoparticles) during gestation; susceptibility factors to develop lung diseases in adulthood (Environment Health Perspect 2017, Nanotoxicology 2017)?
- NP physico-chemical characteristics such as diameter, length, surface properties or chemical nature are critical determinants of their effects on lung inflammation, oxidative stress and autophagy, as well as their intracellular modification (Autophagy 2018, Particle & Fibre Toxicol 2016, 2013, 2011, 2010, AJRCMB 2013)