Publication in the Lancet Public Health of a study by Emilie SBIDIAN’s EpiDerme Research Unit to estimate the prevalence and incidence of vitiligo on a global, regional and national scale.
 Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by depigmented skin patches, which can pose significant psychosocial challenges, particularly in dark-skinned individuals. Despite its impact on quality of life, there is a lack of standardized global epidemiological data.
Vitiligo is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by depigmented skin patches, which can pose significant psychosocial challenges, particularly in dark-skinned individuals. Despite its impact on quality of life, there is a lack of standardized global epidemiological data.
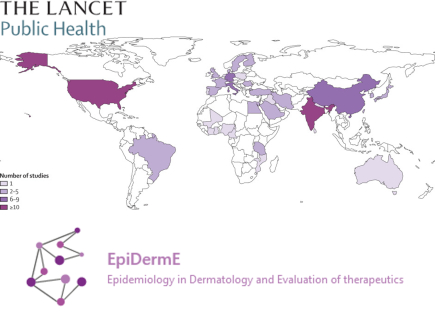
Dr. Jennifer AKL and Prof. Khaled EZZEDINE, UR EpiDerme of Emilie SBIDIAN who will join IMRB in the next term, have sought to fill this gap by publishing a study in the March 26, 2024 Lancet Public Health. The team conducted a systematic review and modeling analysis to estimate the prevalence and incidence of vitiligo globally, regionally and nationally by conducting a comprehensive search of nine digital libraries (PubMed, Embase, Web of Science, Scientific Electronic Library Online, KCI Korean Journal Database, Russian Science Citation Index, Western Pacific Index Medicus, Informit, and Health Research and Development Information Network) from inception to May 25, 2023.
This study highlights the need for more research in under-represented regions and populations in order to effectively tackle the global burden of vitiligo. It was supported by WHO – World Health Organization, andILDS – International League of Dermatological Societies.
Access to the article published in Lancet Public Health

